
The financial world is always changing, and one of the latest trends causing a stir is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). With the increasing popularity of cryptocurrencies, central banks across the globe are considering the possibility of creating their own electronic currencies.
In this article, we will explore the concept of Central Bank digital currency, its history, and purpose, the various types of CBDCs, and their practical uses. We will also examine how they are poised to transform the realm of banking, and we’ll discuss the benefits and challenges they present. By the end of this piece, you’ll have a clear understanding of this topic and its potential impact on the future of finance. Central bank money, including physical currency issued by the Federal Reserve, plays a crucial role in the implementation of CBDCs.
Whether you’re a financial expert or simply curious about cryptocurrencies, this article is designed to provide valuable insights. will provide valuable insights into this emerging trend. So, let’s explore the world of CBDCs together!
What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
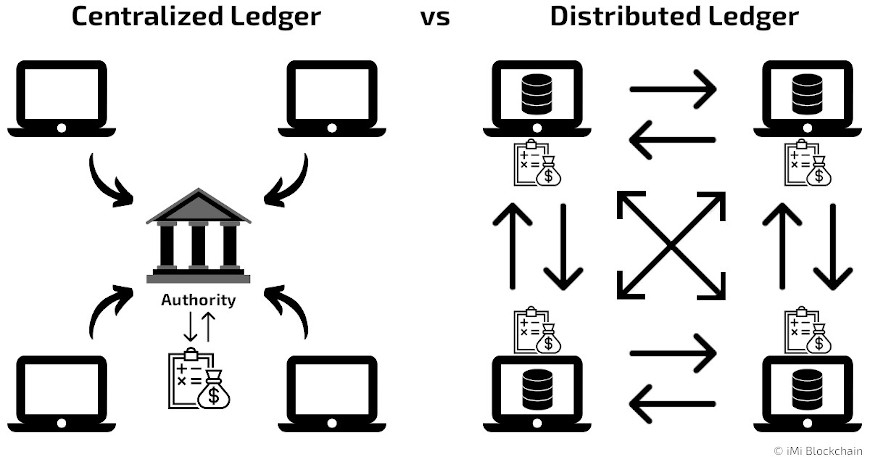
Central Bank Digital Currency is a digital currency or electronic money created by a central bank. The world of money and banks is about to change a lot because of distributed ledger technology which enables CBDC.
A lot of people are talking about Central Bank digital currency these days. But there are various digital currency types around. And because they could make banks work better and make our money safer when we use them. But there are also some problems that come with using it, like making sure they follow the rules and keeping them safe from bad people. We want to tell you about the good and bad things about it and see if they will become the future way we use money.
Share this Image on Your Site:
The people who run the Federal Reserve in the United States are thinking about Central Bank Digital Currency too. They made a discussion paper to examine the pros and cons of a potential use. They even sought public feedback on a range of topics related to CBDC. The Federal Reserve is committed to hearing a wide range of voices on these topics. They want to hear from lots of different people on this topic, including all Americans, as they believe that a U.S. digital dollar should be functional and provide a good customer experience so that all Americans can truly benefit.
In the United States, some adults don’t have a regular bank account. In fact, about 5% of adults didn’t have one in 2020. An additional 13% of U.S. adults who had bank accounts, instead used costly alternative financial services like money orders, payday loans, and check-cashing services to handle their money. This is why a central digital currency could help.
The European Central Bank found that about 10% of households in six big European countries have electronic money already. Central Bank Digital Currency is like a special kind of money that the central bank makes, and you can use it to buy things, save money, or make investments. It’s really safe because it comes from the Federal Reserve, and you don’t have to worry about it losing its value or not being accepted. It’s designed to be easy to use and safe. For example, the digital pound would be a new kind of money made by the Bank of England, and people could use it for their everyday spending, just like banknotes. The Bank of England has published a Consultation Paper to explore the need for the digital pound and propose a set of design choices for it.
The Evolution of Central Bank Digital Currency
CBDC, which stands for Central Bank Digital Currency, is the next step in the development of digital money. Its main goal is to make it safe and easy to trade online. A big part of this plan is to ensure that people who don’t have access to traditional banks can still use it. Additionally, CBDC could help save money and make it clearer how the domestic payment system works within the United States, which would be good for both regular people and businesses.
However, bringing in CBDC needs careful thought to make sure it doesn’t cause problems with how banks work and what the central bank is responsible for. It’s important to consider these things to ensure the change goes smoothly and that Central Bank e-Currency can bring all the good things it promises to the general public.

Unlock Your Business Potential with Certified Blockchain Consulting!
Dive into the future of technology with our team of certified blockchain experts. Simply pick the service you need:
Personalized Advice – tailored to your business needs.
Comprehensive Training – for you and your team.
Development Services – innovative solutions from the whitepaper to the finished blockchain.
Programming – with capabilities and tools to succeed.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS TODAYThe Different Types of CBDCs
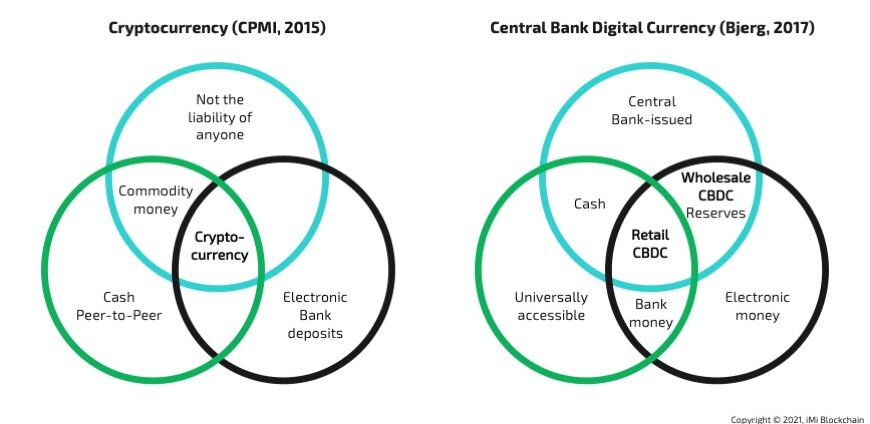
CBDCs come in two types: wholesale and retail. Wholesale CBDCs are for banks to trade and settle transactions, while Retail CBDCs are for regular people to use in their everyday purchases. These digital currencies could change how we make payments and help more people access banking services, even if they don’t have a bank account. They are like modern, safe ways to handle money online, and they might make banking faster and more secure.
Wholesale vs. Retail CBDC Currency
Wholesale CBDCs are made for transactions between banks in the financial sector, while retail CBDCs are meant for regular people to use in their everyday transactions. The Retail one aims to replace physical money in personal and business dealings, offering advantages like improved efficiency and safety. The Wholesale one can streamline large-scale financial transactions. Both wholesale and retail CBDCs have the potential to change the banking industry.
Various models of this CBDC money are being put into action, like the account-based model in the Eastern Caribbean and the permissioned blockchain network model being considered by the European Central Bank for distributing a digital Euro.
How will CBDCs Reshape the World of Banking?
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are poised to transform the banking landscape, serving as a bridge between conventional banking systems and digital currencies. These digital forms of money, similar to stablecoins, provide a different option from cryptocurrencies while also maintaining stability in financial services systems, which, in the end, helps create a financial world that includes more people. CBDCs are the digital form of a government-issued currency that isn’t pegged to a physical commodity, making them a secure and reliable means of exchange.
Share this Image on Your Site:
Impact on Traditional Banking
Central Bank Digital Currencies could shake up the way banks work because they offer a direct link to central bank funds. This might mean that banks have to change how they do business to stay competitive in a CBDC world. Furthermore, they can make international transactions smoother and lessen the need for correspondent banks, which could make the financial industry work better. But, banks will also have to spend on tech stuff to make this fit in. Even though there are difficulties, CBDCs could enhance the stability of the financial system by cutting down on risks from other parties.
Advantages of Central Bank Digital Currencies
Central Bank Digital Currencies have several benefits when it comes to digital payments, including better accessibility. To put it simply, CBDCs can make digital transactions faster and more efficient, changing the way we do business. They also provide better security than physical money, which means there’s less chance of fake money or theft. Plus, CBDCs can help more people join the world of digital payments, even if they don’t have a traditional bank account. This helps folks who couldn’t use regular banks before. CBDCs also make it easier to see where money is going, which makes it harder for people to do illegal things with it.
Lastly, CBDCs are a trustworthy kind of digital money because they’re backed by the central bank, so you can be confident they have value. There are potential benefits to establishing these electronic currencies, such as greater accessibility, but they aren’t without risk. Read on to learn more.
Increased Efficiency
Central bank digital currencies have the potential to bring about significant changes in financial transactions, making them faster and more secure. With CBDCs, transactions can happen instantly and in real time, eliminating the need for long waiting periods. Furthermore, CBDCs reduce the dependence on middlemen, making the process smoother and less expensive, thus contributing to financial stability.
The use of cryptographic techniques also improves the safety and reliability of transactions, preventing fraud and counterfeiting. Additionally, CBDCs make it easier to follow regulations like anti-money laundering and know-your-customer requirements. As a liability of the Federal Reserve, CBDCs provide a more efficient and secure way to carry out financial transactions, benefiting both individuals and businesses.
Challenges in Implementing CBDCs
Creating rules and guidelines for how Central Bank Digital Currencies can be used is a very important task. It’s essential to deal with the worries about security issues like hacking and cyberattacks to make sure the digital money system is safe. Furthermore, we must think carefully about and find solutions for privacy concerns when it comes to collecting and using people’s personal information.
Setting up CBDCs might also mean spending a lot of money on the technology and systems needed to make them work. Making sure different CBDC systems can work together smoothly is another problem we have to solve for CBDCs to be used effectively.
Regulatory and Security Concerns
Privacy concerns are a big factor in why people are using cryptocurrency more. There are rules that need to be made to make sure things like keeping the economy stable and making sure people are safe with their money are taken care of. When it comes to Central Bank Digital Currencies, they need to be really safe so that nobody can get into them without permission and so that people’s private information is protected. It’s important for there to be rules and people checking to make sure that bad things like money laundering and terrorist financing don’t happen.
Financial institutions play a crucial role in ensuring compliance with these rules and regulations. When different countries work together, it can help solve problems that happen when money moves between countries. But, when making CBDCs, it’s tricky because you want to protect people’s privacy but also make sure things are clear and open. By thinking about these rules and safety issues, can make the change to CBDCs easier and safer for everyone.
Are CBDCs the Future of Monetary Exchange?
Many countries are working on creating digital currencies controlled by their central banks, known as CBDCs. These digital currencies might become the way we use money in the future. They have the potential to change how we buy and sell things, making transactions easier and safer. CBDCs could make the financial world better, but whether they become popular depends on things like rules and if people like them, so we don’t know for sure what will happen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, central bank digital currencies have the potential to reshape the world of banking by making financial transactions more efficient and secure. With CBDCs, traditional banking systems may need to adapt to the changing landscape of digital currencies. However, implementing CBDCs comes with its own set of challenges, including concerns about rules and security that need to be addressed.
Despite the challenges, CBDCs offer numerous advantages that can revolutionize how money is exchanged. To stay informed about the latest developments in CBDCs and other financial innovations, subscribe to our newsletter below for regular updates and insights. Together, we can explore the future of digital currencies and their impact on the global economy.
Learn all about CBDCs!
Book a 1to1 Training
Watch our Webinars
Enroll in Online Courses
Learn about Cryptocurrency
Become a Professional
Free CBDC News!
Get news about CBDCs.
On top, you’ll get our free blockchain beginners course right away to learn how this technology will change our lives.
FAQ
What does CBDC mean?
CBDC stands for Central Bank Digital Currency. It’s a digital form of a country’s official currency, issued and regulated by the central bank, designed for use in electronic transactions and the broader financial system.
How does CBDC differ from Cash or Creditcard?
CBDC, issued by the central bank, is a digital currency that differs from traditional forms of currency. Unlike physical money, CBDC enables instant transactions and cross-border payments. It offers enhanced transparency and security, although challenges such as privacy concerns and new infrastructure are also present.
How might CBDC impact the global economy?
CBDCs could revolutionize the global economy, boosting inclusion and reducing costs. They might reshape banking and aid monetary policy, but privacy, security, and stability concerns must be tackled.
How does CBDC differ from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
CBDCs, regulated by central banks, provide faster, secure, and transparent transactions, aligning with government regulations. In contrast, decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin challenge traditional financial systems.
How would the introduction of a CBDC affect individuals and businesses?
CBDCs could transform transactions, providing speed and cost-efficiency, and boosting financial inclusion. Yet, policymakers must address privacy issues and monetary policy risks.
Is CBDC a Cryptocurrency?
CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency) is a digital form of a nation’s currency issued by the central bank. While it shares some characteristics with cryptocurrencies, CBDC is not the same. It’s a regulated and centralized digital currency, unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which are decentralized and not controlled by any central authority.


