
If you’ve been keeping up with the latest technology trends, you might have heard about something called distributed ledger technology (DLT) and how it could change different industries. But what exactly is DLT, and how does it work?
In this blog post, we’re going to explain the basics of DLT in a way that’s easy to understand, even if you’re new to the world of blockchain. We’ll talk about how it’s different from regular databases, go over its advantages and how it can be used, and share some real-world examples to help you see why it’s important.
So whether you’re into tech stuff or just want to learn more about how digital transactions might change in the future, this blog post is for you. Let’s get started and learn about DLT together!
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
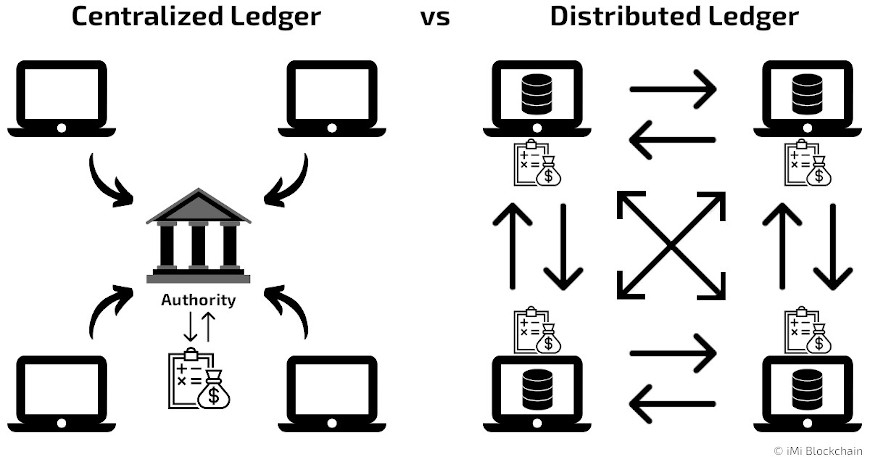
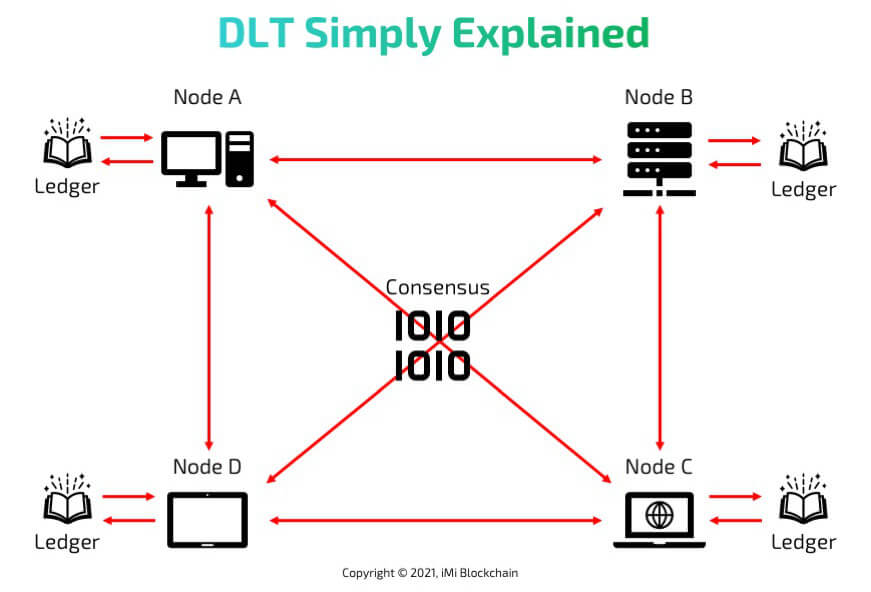
People also asking what is DLT technology, but to be precise, Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a kind of digital database tech meant to safely record and save transactions across several computers connected to a network. You might have heard of blockchain, which is closely related to DLT, but it covers a wider array of distributed ledger systems.
Share this Image on Your Site:
It’s crucial to understand that although blockchain is among the most famous versions of distributed ledger technology, not all DLTs work the same way with blocks in a chain. We have another post where we explain in detail what Blockchain vs. Distributed Ledger Technology means. You will see that there are some crucial differences between these two terms. But for now, let’s continue to focus on this.
Some use different types of data structures and agreement methods, depending on what they need to do. The term “updating of records” is frequently used as a broader way to talk about all sorts of decentralized ledger (bookkeeping) systems, not just blockchain. These decentralized ledger systems, including distributed databases and registries in different locations, ensure that all copies of the ledger are identical, thereby maintaining transparency, security, and cryptography.
DLT Basics
To understand the basics of DLT we have to know some important key factors, which are:
- Decentralization: Instead of one central place, DLT shares track of transactions on many computers
- Transparency: DLT is designed for trust and where everyone in the network can see the transaction history
- Security: DLT is very secure and data is super safe
- Consensus algorithm: DLT uses “Proof of Work” or “Proof of Stake” mechanisms
- Immutable: Once something is written on the ledger, it can’t be changed or deleted
Share this Image on Your Site:
Overall, Distributed Ledger Technology can change how we handle transactions and data in many fields. It offers more transparency, security, and efficiency.
DLT vs. Traditional Centralized Systems
Distributed Ledger Technology is quite different from traditional centralized systems in various important ways. Knowing what is distributed ledger technology makes it easier to understand the following differences:
- Architecture: In traditional centralized systems, there’s a single entity in control with the risk of a single point of failure. But not with DLT. Data and transactions are spread out with encryption across many computers or nodes in a network and each stores a copy of the ledger with simultaneous access in real-time.
- Control: The power of a central authority is off. On DLT networks participants work together to validate transactions and make decisions.
- Transparency: In centralized systems, you can keep information hidden. DLT tends to be very transparent to build trust and accountability.
- Security: Usually, with a single server we have a single point of failure. DLT is more secure because it is a decentralized system.
- Efficiency: Traditional systems can be fast and scalable because they are centralized. Modern DLT systems might not be as fast because they require a consensus mechanism.
- Trust: Before, trust often relied on legal and regulatory frameworks. In DLT, trust is based on the technology itself and the consensus process.
DLT, particularly in the form of blockchain technology, has gained attention for its potential to disrupt various industries. It offers a more transparent, secure, and decentralized alternative to traditional centralized systems. It’s essential to understand, though, that this isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution.

Unlock Your Business Potential with Certified Blockchain Consulting!
Dive into the future of technology with our team of certified blockchain experts. Simply pick the service you need:
Personalized Advice – tailored to your business needs.
Comprehensive Training – for you and your team.
Development Services – innovative solutions from the whitepaper to the finished blockchain.
Programming – with capabilities and tools to succeed.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS TODAYTypes of DLT and Applications
Distributed Ledger Technology includes different systems and technologies that make it possible to securely record transactions and data in a decentralized manner.
As you know now what is distributed ledger technology, let’s explore some of the main types of DLT:
Bitcoin, Blockchain, Cryptocurrencies
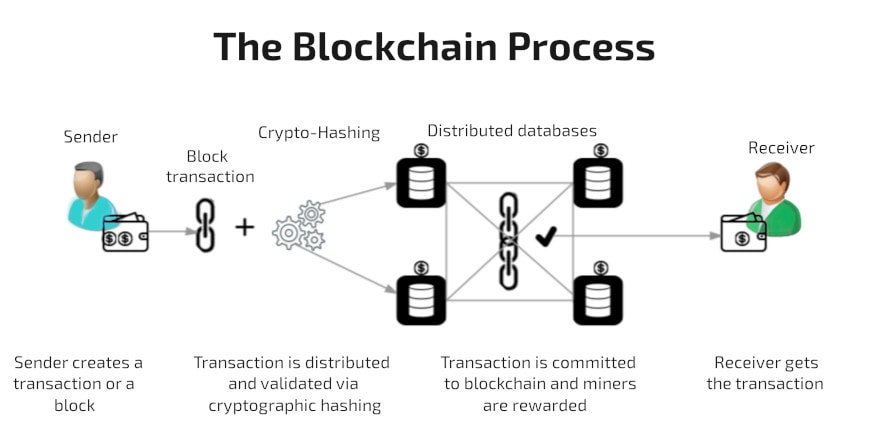
Blockchain, originally designed for Bitcoin, is now a widely recognized distributed ledger technology. Beyond cryptocurrencies, it’s applied to various purposes like distributed computing and maintaining secure, peer-to-peer networks. Unlike traditional centralized ledgers, blockchain operates on numerous computers or nodes, ensuring robust security. Organizations typically stored data separately and centralized it periodically. In contrast, blockchain maintains a decentralized, consensus-driven database with cryptographic signatures, exemplified by Bitcoin. BTC maintains a distributed database in a decentralized way.
Share this Image on Your Site:
Think of transactions as puzzle pieces that form blocks, which are linked together in a chain, creating a time-ordered record. Blockchain, a well-known DLT, uses Proof-of-Work (PoW) where miners compete to validate transactions and create blocks via complex math, requiring significant computational power. While resource-intensive and energy-consuming, PoW ensures network security and immutability. Blockchain has transformative potential in industries like finance, supply chains, and healthcare, as it securely stores and verifies information without intermediaries, gaining global attention.
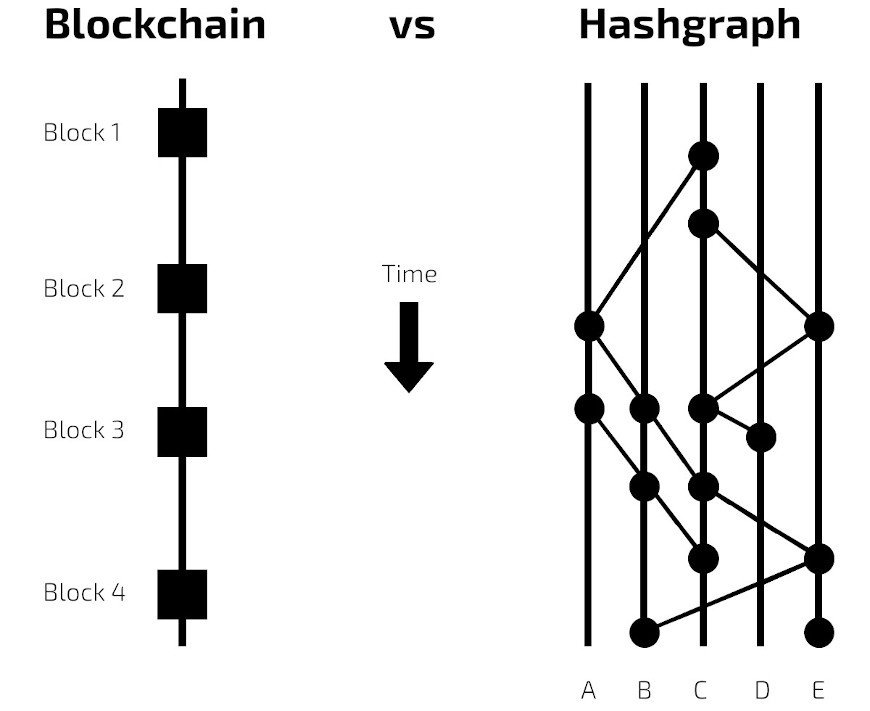
Other types – DAG and Hashgraph
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) offers a different approach to DLT, one that doesn’t depend on conventional blocks and chains. Instead, it employs a graph structure in which each transaction directly refers to multiple previous transactions. This eliminates the need for miners and can potentially enhance scalability and transaction speed. IOTA serves as an example of a cryptocurrency that employs DAG technology.
Another type of DLT that is gaining attention is Hedera Hashgraph. Hedera Hashgraph has achieved the gold standard of security in distributed ledger consensus mechanisms, which is asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance (aBFT), and is the only distributed ledger to date that has formally proven this quality.
Share this Image on Your Site:
DAG and Hashgraph are the most used DLT types next to Blockchain technology. But there are a few more. Today we just name them, without going into details:
Holochain for creating dApps), Tangle for IoT on the IOTA network, Corda for private permissioned enterprise networks, Quorum for consortium blockchains on Ethereum, Hyperledger hosted under Linux, EOSIO if we want to delegate Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Algorand for high scalability and security with speed.
Advantages of DLT – Trust & Transparency
Distributed Ledger Technology has gained a lot of attention and is being adopted by many because it has a lot of benefits. Here are some of the key advantages when using DLT:
- Decentralization: This makes the system strong and less likely to be attacked or messed with.
- Security: DLT uses special math techniques to keep transactions and data safe, while the ledger is immutable.
- Transparency: DLT keeps a clear and checkable record of all transactions for mutual trust.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts make transactions cheaper and faster.
- Immutability: Once data is put into a DLT, it can’t be easily changed or deleted, for enhanced accuracy.
- Easy Access: Anyone with an internet connection could join and use it.
- Less Trickery: Improved security settings are available.
- Across the World: DLT makes it easier for people in different countries to do business together.
- Privacy: Open network, but it can also keep things secret with codes and special networks.
- Staying Strong: DLT networks are always working, even if some of the computers or nodes break down.
- Smart Deals: We can do smart contracts automatically and this makes sure agreements are kept.
- Digital Tokens: DLT can make special digital tokens that stand for real things, like land or stocks. This lets people own bits of things and trade them easily.
- Sorting Out Supplies: Supply chains can be tracked in real-time, and people can find out where things came from.
- Follow the Rules: A system can follow the law and keep records with the full history.
- Inventing New Stuff: We can create new business models and change our industries.

Unlock the Code: Master Blockchain Programming!
Dive into the world of decentralized technology with our comprehensive online programming courses. Learn at your own pace and get:
Access – to expert instructors.
Interactive – coding exercises.
Vibrant – community of like-minded learners.
Certified – receive your recognized diploma.
ENROLL TODAY AND TRANSFORM YOUR FUTURE!Challenges and limitations of DLT – More than Scalability
Distributed Ledger Technology, which includes blockchain, has gained a lot of attention for its potential to change various industries. However, it also has several difficulties and restrictions that need to be thought about:
- Scalability is a challenge, while communities working hard on sharding, sidechains, and layer 2 systems to make DLT more scalable.
- Energy Usage is another challenge, but moving to more eco-friendly systems like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) will help.
- Regulations and Laws, because following all these rules can be hard, especially if a project is worldwide.
- Interoperability is also a challenge, and fixing the needs of many people always takes time.
- Security can be a challenge but depends on how we set up a network.
- Privacy is in fact a challenge because DLT was made for transparency and mutual trust.
- Adoption and Learning is a long journey, as big changes going through companies.
- Cost is a huge challenge for small companies and start-ups and DLT isn’t cheap.
- Governance is the last to mention, as transparency and public ledgers come into place.
Even with all these challenges and limits, this technology keeps changing, and people are still studying and working on these issues. To use this technology well, it’s important to think about these things and understand how it can fit your needs.
Examples of DLT Applications
Distributed Ledger Technology is a decentralized and secure way to record transactions and manage static data as well as dynamic data. It has many real-world applications across different industries. Before we delve into the major application types, let’s explore some lesser-known examples:
Share this Image on Your Site:
Like Smart Contracts to help automate contracts by encoding their terms into self-executing code. In real-time, DLT can simplify property transactions. Intellectual Property Management, Gaming, or Virtual Assets became a big thing since we know NFTs (non-fungible tokens). In Energy Trading, peer-to-peer networks can optimize distribution and minimize waste. Legal and Notary Services can manage legal documents and notarization much more easily and ensure the authenticity and integrity of legal papers. Finally, there are Education and Academic Credentials where we can verify and store data simply but safely.
Then we have the big businesses for distributed ledger technologies:
Supply Chain Management

In Supply Chain Management, Blockchain technology, often referred to as DLT, can be harnessed to establish transparent and unalterable supply chains. This innovative approach enables the monitoring of a product’s origin and its entire path, ultimately minimizing deceptive activities and guaranteeing the legitimacy of products. One noteworthy illustration of this technology in action is IBM’s Food Trust, which meticulously traces the origins of various food products. Walmart, the US giant has already implemented such a system.
Financial Services

In the banking and finance industry, distributed ledger technology, such as Hyperledger Fabric, has also found application in trade finance, particularly through the implementation of smart contracts. In 2016, some banks tested distributed ledger systems for payments to determine their usefulness. Central banks around the globe testing CBDCs (central bank digital currencies).
In 2020, Axoni launched Veris, a distributed ledger platform that manages equity swap transactions. The platform, which matches and reconciles post-trade data on stock swaps, is used by BlackRock Inc., Goldman Sachs Group Inc., and Citigroup, Inc.
Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are one of the most well-known uses of DLT. These digital forms of money rely on blockchain technology to ensure safe and transparent transactions between individuals.
International Money Transfers have the potential to make it quicker and more affordable by getting rid of the requirement for numerous middlemen and decreasing the time it takes for transactions to be completed.
Insurance companies, as another financial sector, can streamline their claim processes by automating verification and payouts based on predefined conditions in smart contracts.
Healthcare
In Healthcare, Data Management is where Blockchain technology, specifically Distributed Ledger Technology comes in. It can be employed to securely oversee and exchange patient healthcare records. This guarantees the accuracy and confidentiality of data while permitting authorized individuals to retrieve vital medical details.
Voting Systems and Governance

Blockchain technology can make modern voting systems (e-voting) secure and transparent. It ensures that votes are recorded securely and prevents any attempts to manipulate election results.
In Governments, it can also be applied to safely store important documents like records of land ownership, birth certificates, and business licenses. This helps streamline administrative processes and reduce the potential for corruption.
Identity Verification is key for a secure, tamper-proof digital identity for individuals, serving purposes like safe online authentication, access control, and reducing identity theft.
Considerations when Choosing DLT
Choosing a Distributed Ledger Technology solution for your business is a crucial decision with potential consequences. DLT, like blockchain, provides benefits like transparency, security, and efficiency. Before deciding, it’s essential to assess your specific needs and requirements. Here are key factors to consider when selecting a solution for your business, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
One crucial factor to consider is the level of automation in this solution, which streamlines processes, reduces manual intervention, enhances efficiency, and boosts productivity. Additionally, this technology empowers individuals to control their personal information by selectively sharing records and limiting access, enhancing time efficiency and security. The decentralized approach improves network efficiency and security by enabling transaction validation within the network, eliminating single points of failure and attractive targets for hackers as found in centralized ledgers.
There are so many things to consider, before choosing DLT. Hence, it is almost a must to get advice from a reputable DLT consultant to ensure you don’t forget anything. Is Proof of Concept already in place? Ensure Long-Term Viability! Create a proper Architecture of Data Management and Storage.
Finally, you should also be prepared to measure and set User Experience, Training and Skill Set, Backup and Recovery, ensure you go on Open Source, check all Legal and Intellectual Properties, and create Auditability and Transparency.
Conclusion
This guide explains the basics and answers the question of what is distributed ledger technology. DLT has been around for a long time, but it’s recently become even more useful. Learn about it and how it’s changing various industries.
By carefully considering all these factors, you can make an informed decision when choosing a solution that best fits your business or organization’s needs. It’s often advisable to consult with experts and conduct thorough research before making a final choice. If you want to know more about distributed ledger technology or have questions, you can schedule a free consultation today with the DLT experts from iMi Blockchain.
Learn Distributed Ledger Technology!
DLT Training in Small Classes
Webinars about DLT Coding
DLT Courses at University Level
Get Free DLT Tips!
Get monthly tips on how DLT can help your business.
On top, you’ll get our free blockchain beginners course right away to learn how this technology will change our lives.
FAQ
When was distributed ledger technology invented?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) was first invented in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. These two researchers implemented a system where document timestamps could not be tampered with. The first proof of concept was published in 2009 by a ghost named Satoshi Nakamoto who created the Bitcoin blockchain.
Why distributed ledger technology?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) can reduce the costs of transactions. Furthermore, it is more secure due to decentralized storage. Last but not least, a DLT system is very hard to manipulate and it eliminates the need for a middleman or third party with administration functionality.
Is blockchain distributed ledger technology?
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology. Blockchain is a sequence of blocks and DLT does not require a chain. In theory, distributed ledgers offer better scaling options than blockchain applications.
How to learn distributed ledger technology?
If you want to learn distributed ledger technology it’s highly recommended that you study computer science at a top-ranked university. It could be MIT, Stanford, Cambridge, Oxford, Nanyang, or ETH Zurich. If this is not possible, your can enroll in online DLT courses at the iMi Blockchain Academy.
Is DLT better than Blockchain?
DLT is a broader concept that includes blockchain. Whether DLT is better than blockchain depends on the specific use case. Blockchain is a type of DLT known for its security and transparency, while DLT encompasses various ledger technologies, each suited to different applications.
What is the difference between DLT and DEFI?
DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology) is a broader concept that includes blockchain technology, while DeFi (Decentralized Finance) refers specifically to financial services and applications built on blockchain and DLT, aiming to eliminate traditional intermediaries in finance.


