
Have you heard of smart contracts? They’re a new thing in the world of digital technology and they’re changing how we do things online. So, what are smart contracts?
Let’s find out! In this article, we’ll learn about these digital agreements and how they work in the online world. We’ll talk about the history of these online contracts, how they work, and how they can be used for more than just digital money.
Many experts, like lawyers, are wondering how to use them too. If you’re curious keep reading, and we’ll have smart contracts explained as well as how they work.
What are Smart Contracts on the Blockchain?
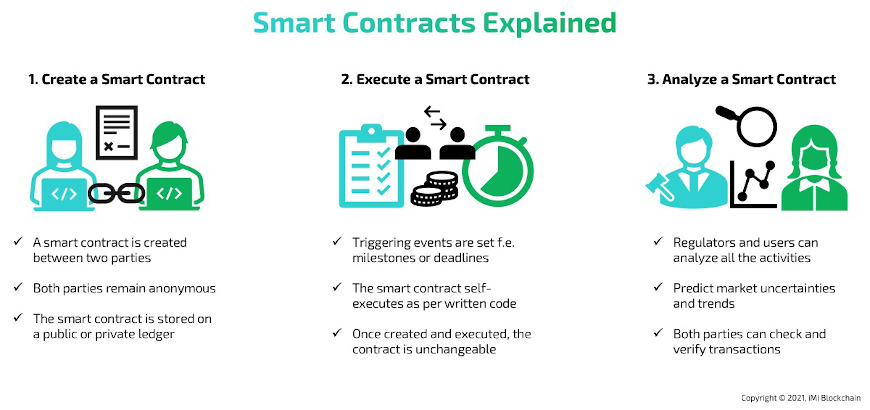
The smart contract technology is like a regular contract, but it’s all done on the computer. These contracts have rules, and when the rules are met, they automatically execute actions according to the terms of a contract. For example, if you and a friend make a bet using such a contract, the winner would automatically get the money when the bet is over, without needing someone to check who won.
Share this Image on Your Site:
Such a clever contract is like a digital promise. Imagine you and your friend promise to swap toys. Now it’s like writing that promise on a computer, using smart contract blockchain, so it can’t be broken. Unlike regular written promises or spoken ones, these agreements are online.
Some digital promises need people to check who made them using special computer programs. But with digital contracts, you don’t always need a person in the middle. The computer checks everything for you. Sure, it’s a bit technical. You will have to learn about a thing called Solidity and later you will also hear about NFTs.
What’s cool about these online contracts is that they’re easy to use. Even if you don’t understand all the computer stuff behind them, it’s like using a computer or phone: you don’t need to know how it’s built to use it!
What Blockchain has Smart Contracts?

You might have heard of Ethereum, the best-in-class blockchain to use smart contracts. But there are other options too, like EOS, Cardano, NEO, and QTUM. Each of these has its own cool features. Just like when a guy named Buterin made Ethereum in 2013, these newer technologies are also getting better and better.
Blockchain is like a digital ledger or notebook that keeps track of transactions. Think of it as a chain of blocks, where each block has information. One cool thing it brought us is called a “smart contract”. The blockchain model was invented back in 2009. Smart Contracts blockchain explained is as simple as adding both technologies together.
There’s a special place called Ethereum where lots of these online contracts live. People can make apps there using these digital agreements, which can help in things like banking, insurance payment, shipment, tracking goods, selling houses, and more. Because of these online arrangements, things can be done quicker, cheaper, and more honestly.

Unlock Your Business Potential with Certified Blockchain Consulting!
Dive into the future of technology with our team of certified blockchain experts. Simply pick the service you need:
Personalized Advice – tailored to your business needs.
Comprehensive Training – for you and your team.
Development Services – innovative solutions from the whitepaper to the finished blockchain.
Programming – with capabilities and tools to succeed.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS TODAYSmart Contract Meaning
A smart contract means having a digital agreement that can work by itself without needing someone to check on it. Imagine two friends making a deal, and instead of relying on another friend to make sure it’s kept, there’s a computer program that ensures the deal is done.
Share this Image on Your Site:
These contracts have become more popular because of something called blockchain technology, which reinforces security, transparency, and trust between signatories. With blockchain technology, these online agreements have the power to execute and enforce themselves autonomously and automatically, based on a series of programmed parameters. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces the risk of misunderstandings, falsifications, or alterations.
Additionally, they have evolved far beyond underpinning a virtual currency, such as Bitcoin, and are now used for various transactions and agreements, including complex transactions. For example, such a contract could initiate a fund transfer with a third party to verify that the transfer took place. We hope we have smart contracts explained and also put together the smart contract blockchain meaning in simple words.
History of Smart Contracts
“Smart contracts explained” also means to look at their history. Here’s their story in a nutshell:
Idea Phase: Transparency through Crypto
The idea of smart contracts isn’t super new. A guy named Nick Szabo talked about it way back in the 1990s. He imagined a world where contracts (agreements between people) could be turned into computer code by using cryptography (aka crypto) and automatically executed.
The Birth of Bitcoin and other Cryptocurrencies
Fast forward to 2008. Someone (or some group) named Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin, the predecessor of Bit Gold. While Bitcoin itself isn’t a smart contract, it introduced the idea of a “blockchain network”. Think of a blockchain as a super secure, public diary where everyone can see the entries, but no one can cheat or erase them. This was a perfect place for such contracts, like Bit Gold, to live.
The Ethereum Ledger
In 2015, a platform called Ethereum was launched by a young programmer named Vitalik Buterin. Ethereum took the blockchain idea from Bitcoin and added a twist: it allowed people to write clever contracts and run them on its blockchain. This was huge! Now, people can create their own digital vending machine rules and use Ethereum smart contracts with a decentralized ledger. Decentralization and autonomous organizations (DAOs) are kings.
The original Ethereum white paper describes the Bitcoin protocol as a weak version of the concept as originally defined by Nick Szabo, and proposed a stronger version based on the Solidity language, which is Turing complete. After the application is written, it is handed off to another team for a security review, which could be an internal expert or a firm that specializes in vetting smart contract security.
Today, the world of digital agreements is growing fast, with many industries looking at how they can use them to make things more efficient and transparent. Why? Because it’s safer, there are fewer human errors, and Hackers do not have a single point of attack.

Unlock the Code: Master Blockchain Programming!
Dive into the world of decentralized technology with our comprehensive online programming courses. Learn at your own pace and get:
Access – to expert instructors.
Interactive – coding exercises.
Vibrant – community of like-minded learners.
Certified – receive your recognized diploma.
ENROLL TODAY AND TRANSFORM YOUR FUTURE!How do Smart Contracts Work?
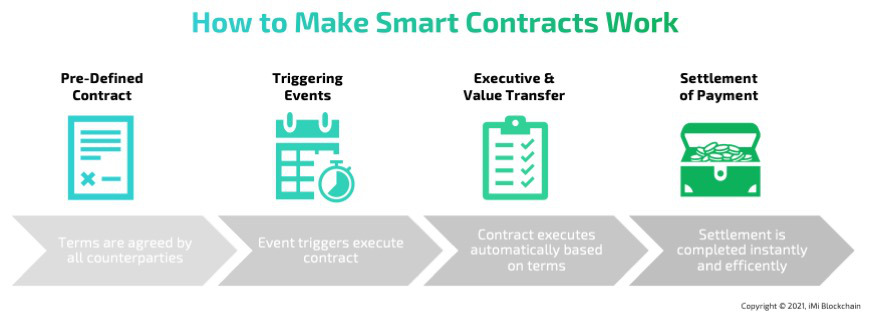
Smart contracts encode business logic and operate on a dedicated virtual machine embedded in an existing blockchain or other distributed ledger infrastructure. This allows business teams to collaborate with developers and define the criteria for such a contract’s desired behavior in response to certain events or circumstances. They can also automate a workflow, trigger time delays, make a single record, and set the next action when conditions are met.
Share this Image on Your Site:
Smart contracts work by following simple “if/when…then…” statements that are written into code on a blockchain. A network of computers executes the actions when predetermined conditions have been met and verified. The best part is, that there is no paperwork to deal with, and no time is spent correcting errors that can occur when filling out documentation by hand. They are also used to automate the execution of an agreement so that all participants can be immediately certain of the outcome, without any intermediary’s involvement or time loss.
Smart contracts started on something called the Ethereum blockchain. There are online contracts on Bitcoin too, but they weren’t really designed for it. Most people use Bitcoin to save money, not on Ethereum. The future lies in the integration of AI algorithms, enabling automation and intelligent systems that can adapt and respond to real-world events in real time.
What is a Smart Contract Example?
So, smart contract what is it? Let’s think of a house that does things on its own, like a home from the future. This home can follow instructions given by a computer program. One popular program says, “If this happens, then do that.” So, your house might have a rule like, “If it’s between 7 a.m. and 10 a.m., turn off the heater.”
But there’s a problem. These rules work online, and sometimes the internet has issues. Also, bad people can break into the online system and change the rules. That’s not good. But there’s a solution called “smart contracts.” These contracts make sure everyone agrees before a rule is followed. Let’s look at a fun example to visualize how this works.
Imagine if your house only lets your sister in when:
- It’s 4 pm on the second Tuesday of the month.
- Someone turns the kitchen light on and off.
- The living room curtains are shut.
- There’s movement seen by the upstairs camera.
- And the house hears a 6-minute phone call with your oldest brother.
Sounds crazy, right? But with smart contracts, this can be set up! The contract checks all these things before letting your sister in. And even if the internet is down, with the right gadgets, the contract can still work and check again when the internet is back.
How to create your own Smart Contract?
Imagine you and your friends want to start a lemonade stand, but you want to make sure everyone follows specific rules when selling lemonade. Instead of just trusting that everyone will remember and stick to the rules, you decide to create a “Magic Contract”. This Magic Contract will automatically make sure everyone follows the rules without any cheating.
This “Magic Contract” is similar to a smart contract system. Here’s how you can create your own Smart Contract:
- Choose a Platform: There are different ones, but Ethereum is the most popular
- Learn a Programming Language: You need to code and Ethereum uses Solidity
- Write the Contract: Set the rules you want for our lemonade example, it could be “For every cup of lemonade sold, 10% goes to buying more lemons”
- Testing: Before making things official, you’d want to test it, to avoid mistakes
- Deploy the Contract: Once you’re done make it official and launch it
- Interact: Now, anyone can follow your rules by interacting with a special software
Remember, creating a clever contract is powerful but also requires responsibility. If there’s a mistake in the contract, it can’t be easily changed, just like how it’s hard to change the rules once you’ve started the lemonade stand. So, always double-check and get some advice if you’re unsure!
In the real world, smart contracts can be used for many things beyond lemonade stands. They can be used for businesses, games, voting systems, and more! The possibilities are endless.
A Simple Solidity Tutorial

Solidity is a programming language used to write smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Think of an online contract as a kind of digital contract that automatically executes actions (like sending money) when certain conditions are met.
Go to Remix, an online Solidity editor and compiler to set it up. There you can write your first contract.
Remember, the world of Solidity and blockchain is vast. As you explore more, you’ll uncover the power and possibilities of smart contract programming.
Pros and Cons of Smart Contracts Explained
imagine you’re playing a game with your friends where you trade cards. You decide to set some rules on how and when a card can be traded. If everyone follows the rules, everything goes smoothly. Now, imagine there’s a magical robot that can make sure the rules are followed perfectly every time. This is what a “smart contract” is like in the world of digital money and business.
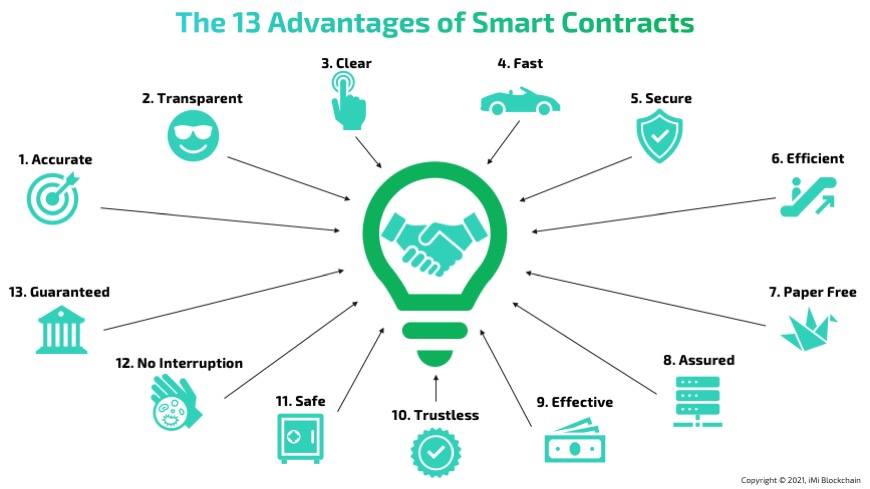
Pros:
- Automated & Trustworthy: Once the rules are set, the contract does everything automatically. This is like having an unbiased referee in your card game.
- Cost-effective: Since everything’s automatic, you don’t need to pay someone to check if the rules are being followed. That saves money!
- Transparent: Everyone can see the rules, so no one can cheat easily. It’s like playing a game where everyone knows the rules and can see them at all times.
- Secure: These contracts are locked and safe. It’s like having a magic safe that only opens when the rules are followed.
- No Middlemen: You don’t need someone in the middle to make sure the trade happens. It’s like trading cards directly with your friend without someone else checking.
Share this Image on Your Site:
Cons:
- Hard to Change: Once the rules are set, it’s difficult to change them. Imagine if you set game rules and then realized there was a mistake. It would be tough to fix.
- Complexity: Building these rules can be complicated. It’s like writing a new game’s instructions, but way more technical.
- Bugs & Errors: If there’s a mistake in the rules, it could cause big problems. Imagine if your game’s rule had a loophole that let someone cheat easily.
- Legal Issues: The laws of countries don’t always agree with how they work. It’s like playing a game that might be allowed at your house but not at your friend’s house.
- Lack of Flexibility: In real life, sometimes we need to make exceptions or understand unique situations. Digital agreements can’t always do this. It’s like a game rule that can’t be bent, even if it makes sense to do so.
So, smart contracts are like magic rule-enforcing robots for the digital world, but they come with their own set of challenges!
Smart Contract Use Cases
Some people didn’t believe that smart contracts could work without humans checking them. Before this innovation, most people only knew about Bitcoin. So, many supporters wanted to show that these online agreements had more uses than just as a type of money.
Share this Image on Your Site:
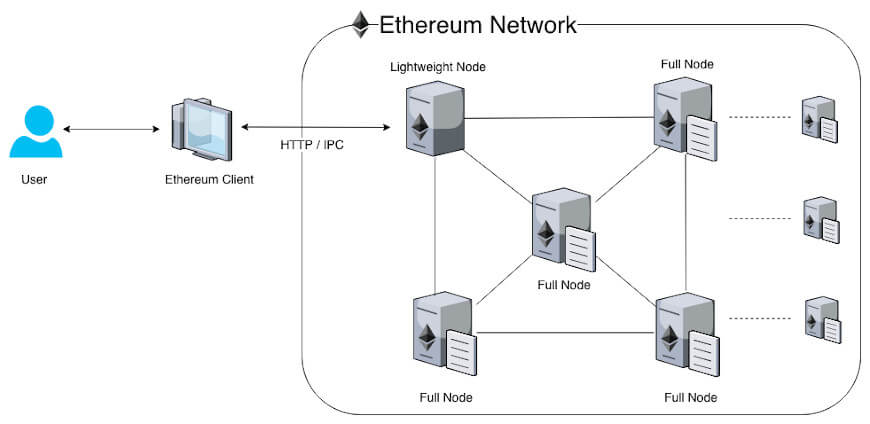
A smart contract is like a digital promise. When everyone agrees on the rules, the computer makes sure those rules are followed. This means we don’t need another person or group to check if everything is correct.
Here, the computer system itself checks everything. Different parts of this system, called nodes, talk to each other to make sure the contract is real and follows all the rules. Smart contracts, such as on Ethereum and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), can be used for things like online votes, digital money, tracking products, and any time we want to trade something online. This security is largely due to the underlying smart contract code and the emphasis on its security.
On Ethereum, for instance, agreements are written in its Solidity programming language, which is Turing-complete. Ethereum-based contracts may be used to create digital tokens for performing transactions. You may design and issue your own digital currency, creating a tradable computerized token. The tokens use a standard coin API. WASM allows developers to create agreements that can run in a web browser and be integrated into blockchains and Oracle. Other distributed ledgers use various programming languages such as C, JavaScript, TypeScript, and Rust.
Final Words
Finally, we have smart contracts explained. They are like special computer programs that can automatically make deals happen without needing a middleman. They’re changing how businesses work by making things faster, safer, and clearer. They can help in many areas like banking or keeping track of things being sold. They can also simplify real estate transactions, which usually involve intermediaries and high transaction costs. By eliminating the need for intermediaries such as brokers to validate signed legal contracts, the use of these digital agreements reduces the risk of third-party manipulation.
With smart contracts, a program enforces the type of contract built into the code, ensuring transparency, security, and sustainability. If you want to know how they can help your business, call us! We have experts who can explain everything to you. Dive into the future and see how your business can get even better with legal templates.
Learn all about Blockchain!
Blockchain Training in small Classes
Webinars about Blockchain
Courses at University Level
Free Blockchain Tips!
Get monthly tips on Blockchain.
On top, you’ll get our free Blockchain beginners course. Learn how this technology will change our lives.
FAQ
Who uses smart contracts?
Smart contracts are used by individuals as well as corporations and governments. Starting from cryptocurrency exchanges, other financial services, e-voting systems, healthcare, supply chain management, and many others.
Are smart contracts legally binding?
A smart contract is like a regular written contract. It has to have the same parts to be legal. Just because it’s on a computer doesn’t mean it’s not real. Everyone involved has to agree to it, and you should be able to see it whenever you want, even later on, for it to count as a real contract.
Can smart contracts be changed?
Smart contracts are like rules (immutable) that can’t be changed once they’re set up. Imagine making a promise you can’t ever break. That’s how these contracts work, and it helps people trust them more.
How many smart contracts on Ethereum?
At the time of writing this blog post, there are 1,536 million smart contracts on Ethereum. A total amount of 2 million user accounts found and 1,14,871,502 Ether supplied on the network.


