Quickly ponder on these questions for a few seconds; How many types of blockchain technology do we have? What is the uniqueness of the different kinds of blockchain technology? If you stuttered while trying to think through the answers to these questions, then this blog post is written for you.
For those a bit conversant with blockchain, there is always a hassle trying to differentiate between the underlying technology powering the Bitcoin blockchain and Corda or other kinds of blockchain. These differences will be highlighted, and we will strive to give a broad exposition to the major types of blockchain infrastructure today.
Let us dive in together.
How many types of blockchain are there?
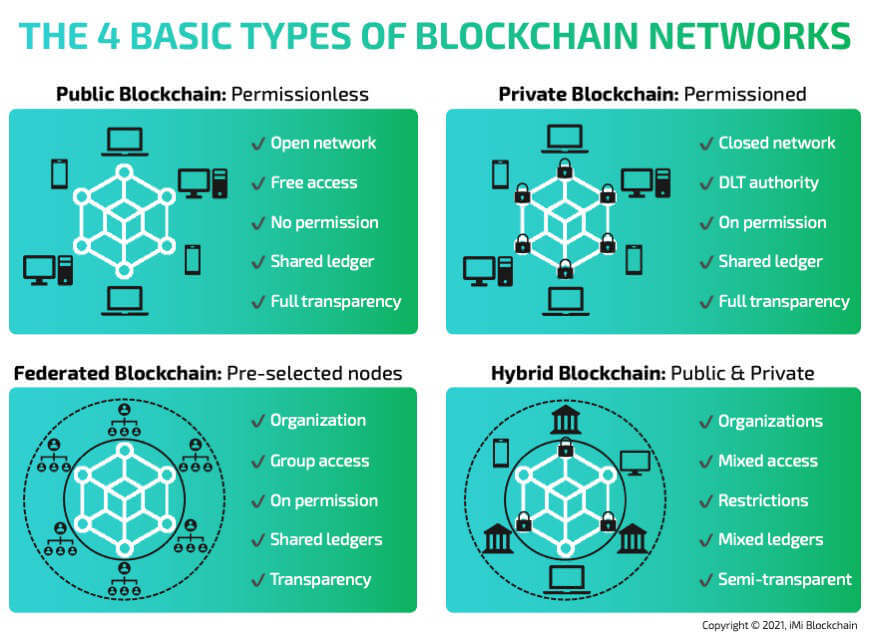
The evolution of decentralized networks has led to the development of different types of blockchain technology. In this blog post, we are going to explore the different types of blockchain there are, including those listed below:
- Public blockchain
- Private blockchain
- Consortium blockchain or federated blockchain, and;
- Hybrid blockchain
In this list of blockchains, each of these has its own merits as we would soon see, and they all have a unique business model or use cases where they thrive perfectly. Read on to learn blockchain technology from the experts.
Why do we need these different kinds of blockchain technology?
The different blockchain types came into existence based on the need to adapt them to function in various industries. It is also meant to fill blockchain applications, your needs, and coding requirements regarding the different types of blockchain platforms available. One of the major uniqueness of the tech is that it is adaptive, and can be integrated into every industry-based to adapt to the specific model the industry operates in. The needs of a supply chain network are different from those of real estate and as such, necessitates the emergence of the different blockchain types. The most important differentiation starts with public vs private blockchain. But let’s compare one at a time.
Share this Image on Your Site:
The broader goal of any project creator can also influence the kinds of blockchain technology to adopt. If there is a need to rollout cryptocurrencies, a public blockchain may come in handy and if the ultimate goal is to keep a part of the data open while another part is kept private, then a hybrid blockchain is ideal.
What are the different types of blockchain technology?
This blog post is a deeper dive into different types of blockchain and what these technologies entail in general. Gaining a broad understanding of the fundamentals of the technology may be essential to appreciate the context on this page. You can check out our earlier article where we gave a good exposition to the question: What are the blockchain technologies?
Here, we would talk explicitly about the different types of blockchain technology, so ride along with us!
Public blockchains
The first of the different blockchains we would be talking about is the public or permissionless blockchain networks. Public blockchains are one of the most popular and they are the foundational frameworks for such digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and many other altcoins.
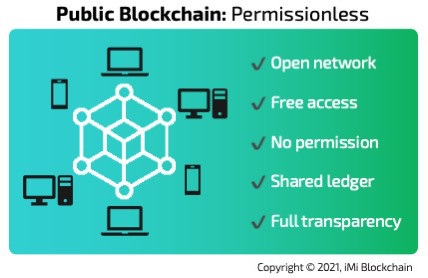
In a public blockchain, anyone can join to make the network operational by conducting transactions and joining the group of validators. Leveraging the web or internet connecting, anyone from anywhere can contribute to the management of the network. In a public blockchain, each participant can be a node operator and keeps a copy of the transactions that take place on the network.
Public blockchains have a decentralized form of governance and the verification of transactions follows a predefined consensus. There is a diverse type of consensus that is used for transaction validation in the public blockchain space and these include but not limited to; Proof of work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Proof of space and time. All great towards immutability.
The proof of work model involves the solving of complex mathematical computations before transactions are registered within the block, it is energy-intensive and is relatively being replaced by the proof-of-stake method featuring the verification of transactions by validators. These validators usually have a stake in the blockchain network, giving them the authorization to contribute effectively to the management of the network.
Public blockchain networks usually incentives participation, and guarantees a high level of security due to the spread of the network participants. Should the node operators, miners, or validators not be motivated enough to work, the public blockchain network will become non-functional and can cause network collapse.
Advantages of public blockchains
Public blockchain network has no restrictive access and is free for anyone to join and participate. While there may be hardware requirements for participants, there are absolutely no defined limitations to who can contribute to the network growth. With all hands on deck in ensuring the optimal functionality of public blockchains, trust becomes a default standard. No one individual can manipulate the entire network.
The incentivization model based on the consensus protocol as highlighted earlier makes network participants give their all to contributing to the blockchain. This enhances the efficiency of the system. In all, public blockchain networks are very secure as one point of attack cannot lead to the collapse of the entire system.
Disadvantages of public blockchains
Slower transaction speed and the lack of scalability tops the list of disadvantages public blockchain network suffers. The presence of numerous participants, many of whom must follow the consensus process to validate transactions usually brings about delays. Since there are no restrictions to the number of participants who can join the network, the blockchain may attain a saturation point where the number may begin to work against the platform.
The energy usage of the PoW blockchain model also makes the entire innovation a source of concern to environmentalists and climate advocates.
Private blockchains
Private blockchains are those designed to operate in a more restricted or closed manner. Private blockchains thrive under a permissioned model in which access to transactions and validations of entries is restrictive. Private blockchains are usually more centralized when compared to public blockchain networks.
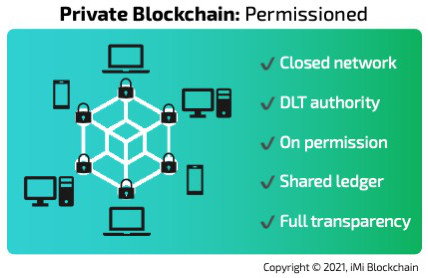
Private blockchains are ideal in an organization that wants to leverage the technology to revamp its internal operations. The organization defines the accessibility requirements to the network, who can conduct transactions as well as who can validate the transactions that take place on-chain. Private blockchains are also ideal for a group of businesses that share similar data in their day-to-day activities. The same way they are used for IoT applications (Internet of Things).
Many may point to the centralization of control as a point of weakness for the private blockchain, however, this does not negate its infrastructural security. Just like others, permissioned blockchain networks are encrypted and features a high level of data cryptography making them less prone to attacks compared to traditional distributed ledger technologies or digital databases.
Tokenization may or may not be an integral part of running a private blockchain, as incentivization may not be necessary, or typically takes other forms. Some popular examples of a private blockchain network are owned by Ripple Labs and BurstIQ amongst others.
Advantages of private blockchains
In a private blockchain platform, the fewer people managing the system makes verification of transactions very fast. Private blockchains are known to attain consensus relatively faster than public blockchains. Scalability in a private blockchain network also comes with no hassles as the number of validators does not necessarily have to increase. This implies that the network speed remains the same as the number of validators may remain constant.
The drudgery in decision-making per ecosystem evolution which always follows a defined process in a public blockchain is eliminated in private blockchains. All these contribute to the increased efficiency of the system.
Disadvantages of private blockchains
Decentralization is one of the hallmarks of every distributed ledger technology and the fact that a central authority makes the final decision in a private blockchain goes against this fundamental tenet. Based on this, private blockchains are neither as trusted as their public alternatives, neither are they as transparent.
A bad decision from the controlling authority may adversely impact the entire system. This makes the security provisions of private blockchains not as strong as other types of blockchain networks.
The same is true for applications from service providers like IBM. Blockchain as a service is completely contrary to the open-source initiative that blockchain is all about.
Consortium blockchain or federated blockchains
Just as the name suggests, a consortium blockchain is such that is managed by two or more individuals, associations, companies, or business outfits. Based on its composition, we can say that a consortium blockchain is a semi-decentralized network in which both public and private blockchain features are inherent. This way, certain data are opened to all the participating members while others are restricted.
Consortium blockchains are also known as Federated blockchains in which the consensus mechanism is attained based on a predefined number of nodes. It should be noted that the fact that consortium blockchains have a public element does not mean it is less of a decentralized network. No single organizations call the shots as all the participating organizations help maintain the trust upon which the network operates.
In all Federated blockchain networks, every node or participating entity can initiate and receive a transaction, while also being empowered to be able to validate transactions in a broader sense. Consortium blockchains bring to life the typical features of a private blockchain while leveraging the security infusion of a public blockchain.
Consortium blockchains are majorly seen in hyperledger fabric, Corda, and Quorum amongst others.
Advantages of Consortium blockchains
Consortium blockchains offer a number of advantages in firms that operate on them. The blockchain attains greater efficiency by combining the features of both private and blockchains. The private parts of the network can easily be taken advantage of to introduce some uniquely tailored features for all participants.
Just like private blockchains, federated blockchains are highly scalable, and are well secured taking note of the benefits offered by their decentralized nature. Per this latter point, consortium blockchains utilize the combined hash power being supplied by each public node. Access control is enhanced as with a defined consensus or governance model, the network can thrive and work for all.
Disadvantages of Consortium blockchains
The risk of onboarding different participants can predispose the network. This is of concern as at least one of the key nodes may be the subject of an attack or malicious action, compromising the entire network. The use of Consortium blockchains may also imply working on a fulcrum as government regulations or any form of inconsistency on the part of any of the participating members can offset the system.
Sharing the features of public blockchains does not imply that it is as secure. Federated blockchain networks still present a few points of weakness for security breaches, that is if any can be pulled off.
Hybrid Blockchains
A hybrid blockchain also utilizes the combined features of private and public blockchain networks. At first glance, hybrid blockchains maintain a huge similarity with consortium blockchains but the difference between both is striking. Unlike consortium blockchains with multiple participants collectively helping to maintain the network, a hybrid blockchain can have a single entity network administrator.
Hybrid blockchains work best when an organization needs some of its data open access and others kept private for in-house use. The multichain model of hybrid blockchain can give room to a lot of allowances, as defined by the owner of the system. The transparency can be open or closed depending on how the rules are set.
The decentralization model in hybrid blockchains is partial, as against that of consortium blockchains in which all participants take full control of the network. Hybrid blockchains give businesses the opportunity to eat their cakes and have them at the same time. This means they can achieve the transparency they need while also keeping their most important data private.
Incentivization is also another key decision every blockchain project that seeks to utilize the hybrid model must decide on. The decision to roll out incentives depends on the business model and whether such benefits will contribute to the growth of the system.
The top examples of hybrid blockchain systems include DragonChain and XinFin’s Hybrid blockchain.
Advantages of Hybrid blockchains
Besides the advantages of hybrid blockchain as described in the features above, these blockchain networks can withstand the popular 51% attacks drawing from their decentralized component. The consensus in hybrid blockchains can be easily modified, or even changed depending on the needs. The ease of scaling a hybrid blockchain is also one of its core benefits.
Disadvantages of hybrid blockchains
The trust rating is low as control is mostly handled by a central authority. Adopting or switching to a hybrid blockchain system by an organization with a type of distributed ledger system may be a hassle. Should incentives be absent in the system operations, external contributors may not be well motivated to participate in keeping the system operational.

Unlock Your Business Potential with Certified Blockchain Consulting!
Dive into the future of technology with our team of certified blockchain experts. Simply pick the service you need:
Personalized Advice – tailored to your business needs.
Comprehensive Training – for you and your team.
Development Services – innovative solutions from the whitepaper to the finished blockchain.
Programming – with capabilities and tools to succeed.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS TODAYOur Conclusion about the different kinds of blockchain
Satoshi Nakamoto popularized blockchains through the launch of the Bitcoin blockchain back in 2009. The cryptic system he created is a public blockchain that always individuals securely send money freely to one another. When the world caught in on the innovations, other blockchains such as the Ethereum network was created, giving room to the emergence of smart contracts.
Over the years, there has been the emergence of other unique blockchain networks, with each alteration seeking to re-engineer the open-source nature of sharing data, or information. Each Blockchain works in unique ways, brandishes a set of merits and demerits as no one system is 100% perfect.
While we highlighted four different types of blockchain technology networks, the industry is new and still expanding, and as we grow to maturity, new inventions may arise, introducing new consensus algorithms for the world to adopt. DLTs and Blockchain technologies have a lot to offer and businesses must choose which model is the best fitting for their businesses. If you need a hand to find the best solution for your business case then book us for a consultation.
Learn the Types of Blockchain!
Book a Blockchain Training
Watch our Webinars
Enroll in Blockchain Courses
Become a Pro yourself
Get free Blockchain Tips!
Get monthly blockchain tips.
On top, you’ll get our free blockchain beginners course right away to learn how this technology will change our lives.
FAQs
How many blockchains are there in the world today?
There are many different types of blockchain technologies today, and as a dynamic innovation, more will be created to work in different industries and under various use cases. However, there are four prominent ones that can be pointed at and they include, public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains, and hybrid blockchain networks respectively.
Who invented blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a few decades old inventions but was popularized with the advent of Bitcoin, created by a developer, or group of developers with the pseudonym, Satoshi Nakamoto. The various kinds of blockchain technology as we have them today are developed by a wide range of individuals and firms to boost their business processes.
What type of blockchain technology is the best?
Every type of blockchain technology is unique in its own way. Each has its own merits and demerits and comparing to know which is best may not be justified as each has its own addressable market or industry where it works best.


