In this blog post, we will be taking a look at the public blockchain vs private blockchain analogy, by highlighting the differences and use cases between these two blockchain systems. It is no longer news that companies in various industries have started integrating blockchain into their digital systems.
The upside of each blockchain system that is being adopted must be considered to know if their businesses can function well with the blockchain system. This article will give a fundamental exposition to both types and we will also compare permissioned vs permissionless blockchain and under which instances they are ideal.
Let us start by extensively highlighting the differences between public and private blockchains. Shall we?
- 1. What is the difference between public blockchain and private blockchain?
- 2. Hybrid vs private vs public blockchain examples
- 3. Hybrid vs public vs private blockchain comparison
- 4. Blockchain vs distributed ledger use case examination
- 5. Public vs private blockchains, which is better? Our conclusion
What is the difference between public blockchain and private blockchain?
The difference between a private blockchain and public blockchain technology is very pronounced in many aspects numbering more than one. While both may share similarities in that the data or transactions are stored within blocks and encrypted using cryptographic keys, their core functionalities are markedly different from each other. It’s all about how to learn blockchain development the right way.
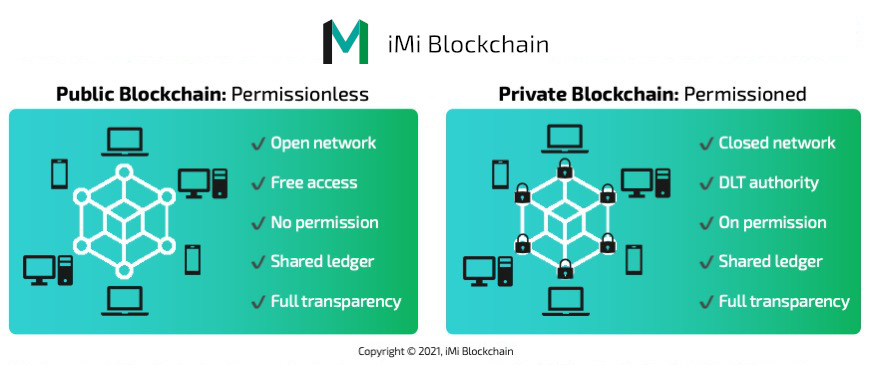
A public blockchain is permissionless, that is, one that grants open access to everyone, irrespective of geographical location. Access control in a public blockchain is open source and brings to life the core tenets of decentralization. No single entity controls the blockchain platform, with every node, or participant sharing the responsibility to keep the network secure and functional. Data handling in a public blockchain is read and write access for everyone and the network offers full immutability, making it impossible to change the recorded data.
A private blockchain on the other hand offers a different consensus approach or model, in that it is permissioned, and deviates from the norm of a typical decentralized network. The data handling within a private blockchain network is usually read and write for a single organization. The privacy of data for in-house use is not uncommon in a private blockchain network and the system thrives based on trust amongst the participating nodes or units that have access to the ledgers.
Both public and private blockchains exhibit efficiency to a certain degree, and when compared to traditional databases. However, when compared to each other, the transaction speed in a private blockchain is faster than that in the public version. The higher the number of contributing nodes, the slower the process of getting a transaction vetted for storage within the blocks. Drawing on the factor also, while public blockchains brandish a relatively low efficiency, private blockchains are highly efficient with the predefined few nodes involved in the decision making.
Amongst the core differences is that public blockchains offer a high degree of trust as it offers full data immutability, as compared to the partial immutability that is typical to private blockchains. In the latter, the organization can decide to adjust some data parameters depending on the situation at hand. This naturally reduces the trust level for these blockchain solutions. Incentivisation through the issuance of tokens is also one of the core hallmarks of a public blockchain. This incentivization may or may not be present in private blockchains.
Share this Image on Your Site:
The consensus algorithm is also a major difference that takes the public vs private blockchain narratives to the next level. While permissioned blockchain networks use consensus algorithms such as Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET), Raft, and Istanbul BFT, the permissionless public blockchains thrive with consensus algorithms such as Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake, Proof of Space and Time, and a number of such alterations. Each of these consensuses for both private and public blockchains has its potential merits and downsides, but they markedly define how the systems run or operate in general.
Scalability is also another aspect where both blockchains showcase their superiority. Private blockchains are generally. The many nodes involved in transaction processes make it difficult to scale up in public blockchains. Should the transactions be increased, the number of nodes that will process them in a private blockchain is defined already, making scaling not an issue to worry about.
The energy consumption requirement of the Proof of Work consensus model in public blockchains is also a downside compared with private blockchains. In all, the order of magnitude of a public blockchain is lesser than that of a private blockchain seeing how much lighter it is. This gives it an edge to provide transactional throughput. When people ask us, “how to invest in blockchain?“, then our first advice is always to invest in sustainable private blockchain projects.
Some organizations usually demand to have a piece of the privacy in a private blockchain as well as the decentralization or other attractive features of public blockchains. This need has birthed a hybrid blockchain system that finds and leverages the points of convergence between these two blockchains. With a Hybrid blockchain system, institutions can choose what part of their data should be made public, and what part should be kept private.
In all, a hybrid blockchain system helps a firm enjoy the closed consensus protocol model, while also coming off with full transparency. A mix of the positive and negative aspects of both private and public blockchains may also be inherent in a hybrid blockchain system.

Unlock Your Business Potential with Certified Blockchain Consulting!
Dive into the future of technology with our team of certified blockchain experts. Simply pick the service you need:
Personalized Advice – tailored to your business needs.
Comprehensive Training – for you and your team.
Development Services – innovative solutions from the whitepaper to the finished blockchain.
Programming – with capabilities and tools to succeed.
TALK TO THE EXPERTS TODAYHybrid vs private vs public blockchain examples
The private blockchain vs public blockchain exposition will best be understood with the analysis of the examples of both. This section will be dedicated to discussing the examples of these unique types of blockchain, and the companies that are utilizing them.
What is a private blockchain example?
A private blockchain is unique to companies seeking ways to utilize the benefits of distributed ledgers to boost their business ecosystem. Examples of industries using a private blockchain consensus algorithm include Ripple Labs Inc’s RippleNet. The RippleNet uses blockchain technology to power a global payments business that is fast, cheap, and secure for all participating institutions.
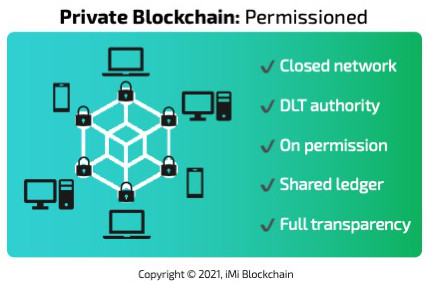
Another perfect example of a private blockchain is the Hyperledger Fabric of the Linux Foundation. Any company can develop its own private blockchain system and customize its functions to suit its needs. Other companies with a functional private blockchain include Corda, IBM, Amazon, and Microsoft amongst others.
What is a public blockchain example?
A public blockchain is such that grants open access to everyone as highlighted earlier. A typical example is seen in crypto products such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and a host of other altcoins. The public blockchain examples also transcend to the sub-alterations of open-source blockchain, which usually gains expressions in smart contracts and decentralized applications.
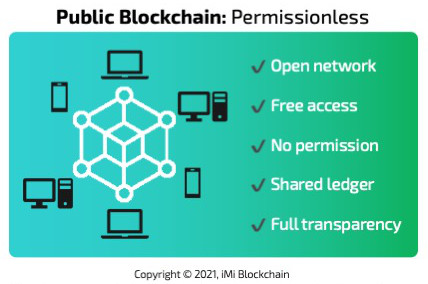
Transactions in these blockchain networks can be viewed and tracked by anyone with access to the internet. On the other hand, if mining is required, then computational power is needed too.
What is a hybrid blockchain example?
A hybrid blockchain is found in the IBM Food Trust, an innovation that seeks to bring together an ecosystem of producers, suppliers, manufacturers, retailers, and others creating a smarter, safer, more sustainable food system for all. DragonChain is also a major example of a hybrid blockchain that offers enterprises the opportunity to deploy innovative solutions.
Hybrid vs public vs private blockchain comparison
The table below will give a brief snapshot of the use case of public blockchain vs private blockchain. These use cases are also defined in comparison with the hybrid blockchains to reflect the interjection between both versions of blockchain infrastructures.
The examples of use cases highlighted below are non-exhaustive as the applications of these technologies are always evolving over time.
| Use Case Examples | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain | Hybrid Blockchain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptocurrencies | YES | NO | NO |
| Payment Infrastructure | NO | YES | YES |
| Asset Management | NO | YES | YES |
| Digital Identity | NO | YES | YES |
| Insurance | NO | YES | YES |
| Real Estate | NO | YES | YES |
| Supply Chain | NO | YES | YES |
| Healthcare Data Storage | NO | YES | YES |
Blockchain vs distributed ledger use case examination
As we talked about use cases of different types of blockchains let us examine these use cases in comparison to DLT vs blockchain. DLT or distributed ledger technology uses the decentralized and shared ledger principle.
1. Cryptocurrencies
By their very nature, digital currencies are designed for public use. There is no censorship to data validation as anyone can conduct transactions, for some others to confirm elsewhere. The parties that keep a cryptocurrency system do not have to know one another, a feature that is antagonistic to the centralization model of private blockchains. As such, the use case of blockchain technology as it borders on cryptocurrencies is most suitable for private blockchain networks.
2. Payment Infrastructures
The payment infrastructures under review here are markedly different from those offered by digital currencies. Private firms like Ripple Labs are taking advantage of the secure, fast, and cheap provisions of blockchains through permissioned networks to roll out a payment infrastructure that is currently being utilized for cross-border cash settlements.
Banks and financial institutions are also using private permissioned blockchain networks to boost cash transactions with entities within their ecosystem. The payment systems that help two or more institutions to facilitate efficient cash transactions are best supported by either a private blockchain or their hybrid versions. There is no need for the whole public to gain access to the data as it is within a closed business circuit. This makes public blockchains unsuitable.
3. Asset Management
Asset management can best be boosted using private enterprise blockchain solutions. Keeping asset data such as cryptocurrencies or other digital securities on the blockchain can help in the efficient management of such data. Asset management firms can use private blockchains to improve their processes, gain the trust of their clients, and maintain transparency to members of the public. Public blockchains are way too elaborate for this use case as data recorded can be viewed by entities who have no direct role in such asset management.
4. Digital Identity
Digital identities can be secured using blockchain technology. Access to the underlying biometric data does not necessarily have to be an open affair for everyone. Data can be stored, managed, and protected using private or hybrid blockchains to give restricted access to a defined set of authorities. The issuance of digital identities can be done by the government or a tech firm. Irrespective of the issuing authority, a public blockchain is not ideal, as access to the stored data by the general public can unduly compromise people’s data.
5. Insurance
Insurance brokers are beginning to integrate blockchain into their businesses to help usher with efficiency, reduce cost and enhance the claims processes. Insurance is a private business, making it ideal to keep its core data in-house. Based on this, insurance data are best secured using private blockchain networks, and not public blockchain networks.
6. Real Estate
Real Estate managers can also utilize private blockchains to boost their business, by keeping the records of clients, land data, and other important information. Depending on the nature of the business, which could either be a private or publicly listed company, the utilization of blockchain technology for managing its data cannot be left at the mercy of unknown node operators. Private or hybrid blockchains, and not public blockchains are the ideal options for real estate firms.
7. Supply Chain
All businesses related to supply chain or logistics will use private blockchains mainly for track and trace reasons. Distributed ledger technology is the best way to store data from cross-border transactions. By keeping the records of clients, land data, and other important information. Private or hybrid ledgers can also be used to replace spreadsheets for sample tracking. A public ledger is not a good option for a supply chain business due to the fact that a lot of confidential data is shared.
8. Healthcare Data Storage
Patients’ data can also be kept secure using encryption or cryptography made possible by blockchain technology. In choosing the choice of the appropriate blockchain to be adapted, think of your data being visible or accessible by anyone or everyone? Sounds awkward? Yes, apparently! This makes public blockchains, not the right option for storing health data.
Private blockchains are ideal for this use case. Access to the data can be enabled for qualified health practitioners to provide informed diagnoses, drugs prescription, and other medical-related procedures. The use of private blockchains will not compromise the stored record, making it all the more ideal.
Public vs private blockchains, which is better? Our conclusion
Public vs private blockchains, which one is better? This is one of the many questions that spur debate whenever discussions about these two unique blockchains are raised. Each of these blockchain networks has the industries or use cases where they thrive better, and seeking to know which one is better may not be a fair representation of their special, individual qualities.
For business owners looking for the right blockchain, they can explore or analyze their differences, pick out their outstanding qualities and relate them with their business models to discover which is the best fit. While private blockchains can easily be adapted to boost business processes making them usable in various industries, there are some unique instances where public blockchains are just the best fit.
Watch webinars on our website to find out more or talk with one of our experts to find the best blockchain solution for your business.
Learn All About Blockchain!
Book a Blockchain Training
Watch our Webinars
Enroll in Blockchain Courses
Become a Pro yourself
Get Free Blockchain Tips!
Get monthly blockchain tips.
On top, you’ll get our free blockchain beginners course right away to learn how this technology will change our lives.


