
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, are really popular right now. They are a kind of digital money. More people are using them, which is why they are growing so fast. But what is cryptocurrency exactly?
Governments and big banks are also starting to notice and use cryptocurrencies because their customers are asking for them.
A lot of people want to learn what is cryptocurrency. They want to know what they are, how they work, and how to use them. This guide will help explain all about it!
What is Cryptocurrency? Our Definition
Have you ever wondered, “What is cryptocurrency?” Maybe you’ve heard of it because of people talking about investing or just out of curiosity.
Well, let’s keep it simple! Crypto is like digital money, but it’s not controlled by the government or big banks. Instead, people who use it control it. It can be used to save, just like how we save money in piggy banks. If you are completely new to crypto, then you should consider taking crypto online classes first.
This article will help you learn more about digital money and how some people use it for investing. We will also give a short intro about cryptocurrency trading for beginners.
Understanding Cryptocurrency for Beginners: Crypto Meaning
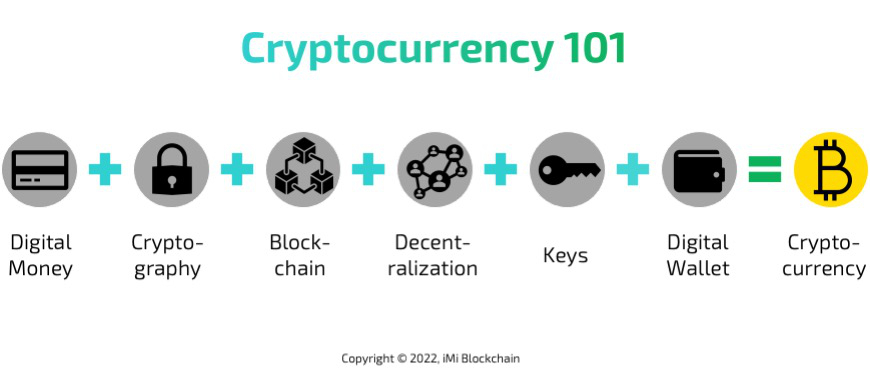
Share this Image on Your Site:
Crypto meaning? Now is a great time to learn what is cryptocurrency, the digital money called “crypto”. First of all, you should be aware of digital currency vs. cryptocurrency. Even though the value of these coins can go up and down a lot, people can also make a lot of money from them. This is why more and more people are getting interested.
Cryptocurrencies are different from digital money. Digital money is just electronic cash that the government controls.
To start learning what is cryptocurrency, you need to know some basic words and what they mean.
In our beginner’s guide, we will talk about seven important terms you’ll hear when learning about crypto meaning.
Cryptography
Cryptocurrencies use special codes to keep their information safe. These codes are very strong because they are based on advanced math and computer skills, making them really hard to break or copy.
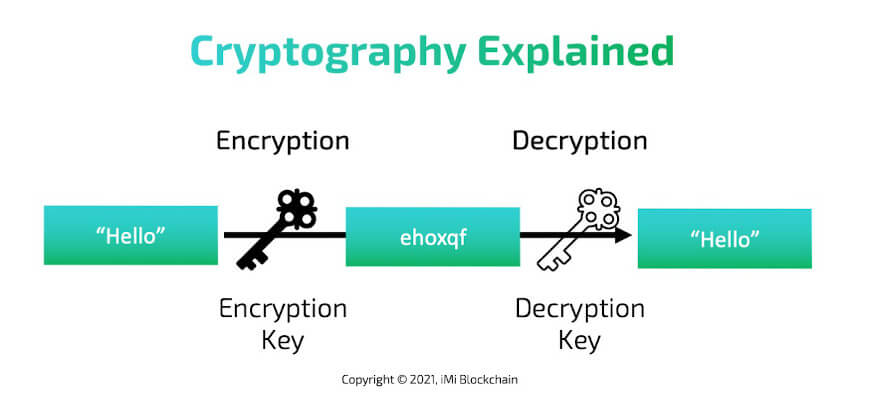
Share this Image on Your Site:
This way, details about trades and the people making them are kept secret. It also keeps the users’ identities hidden, so it’s hard to tell who did what in the network. Cryptography is the first point to understand what is crypto.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is like a digital notebook that keeps track of cryptocurrency exchanges, like when people buy or sell digital money. It makes these exchanges safe, fast, and easy to track. That’s why people are starting to use blockchain for more than just digital money. So, the second step to understanding what is cryptocurrency is its underlying technology.
Share this Image on Your Site:
Every time someone buys or sells this digital money, it gets added to the blockchain in a section called a “block”. To make sure these blocks are legit, they go through a process called “proof of work” or “proof of stake”. There are other ways to check, but these are the main ones. When the blockchain transitioned to proof-of-stake in September 2022, it introduced the concept of staking as an additional duty for validating transactions and opening blocks. In a proof-of-stake model, owners put up their tokens as collateral to maintain the cryptocurrency’s integrity, eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks when funds are being transferred between two entities.
Some popular examples of these digital notebooks are used in digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Cardano.

Unlock Your Crypto Potential: Become a Market Maverick with Expert Coaching!
Are you ready to dive into cryptocurrency but need some advice? With our personalized 1:1 coaching, you’ll learn to:
Understand – the fundamentals of cryptos and how they impact value.
Navigate – through the volatile crypto market with confidence.
Identify – new lucrative opportunities that maximize returns.
Manage – exchanges and risk to protect your investments.
BOOK EXPERT COACHING NOWDecentralization
Blockchain is storing data on every computer within the network. So, many people can have a copy of it at the same time, all over the world. Instead of having all the info in one place, it’s spread out everywhere.
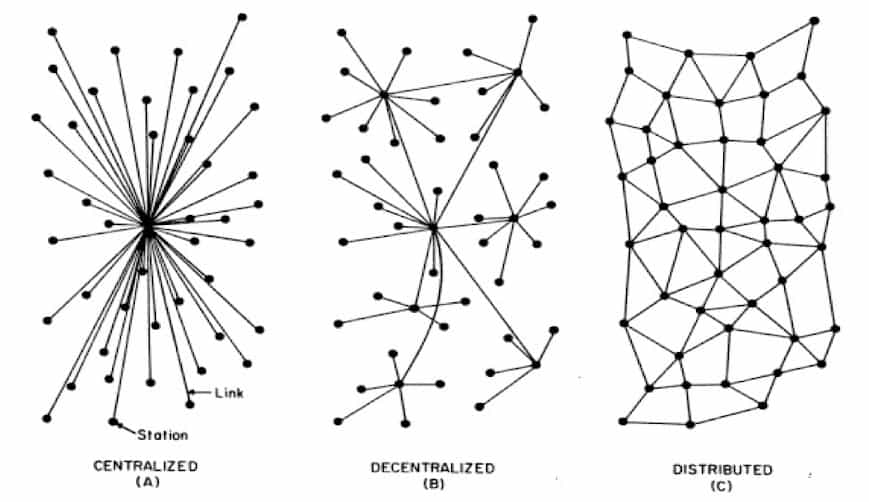
Share this Image on Your Site:
Just like paper money is made and controlled by big banks, digital money (called cryptocurrencies) is used and valued by regular people. Therefore, decentralization is the 3rd point to understand what is cryptocurrency. So how does cryptocurrency work? In short, it works decentralized.
Private Keys
Imagine cryptocurrency is like a special kind of money you keep in a digital box. To open this box, you need a special password called a “private key.” This password also helps make sure no one else can take your money. There’s also another key called a “public key” that works with your private key to keep everything safe, facilitating secure transfers without the need for a trusted third party like a bank or a credit card company. If you lose or forget this special password, you can’t open your box or get your money. That’s why people keep this password in safe places. Some keep it on their computers where there’s no internet, while others might write it down on paper. Encryption plays a crucial role in ensuring the security of these private and public keys.
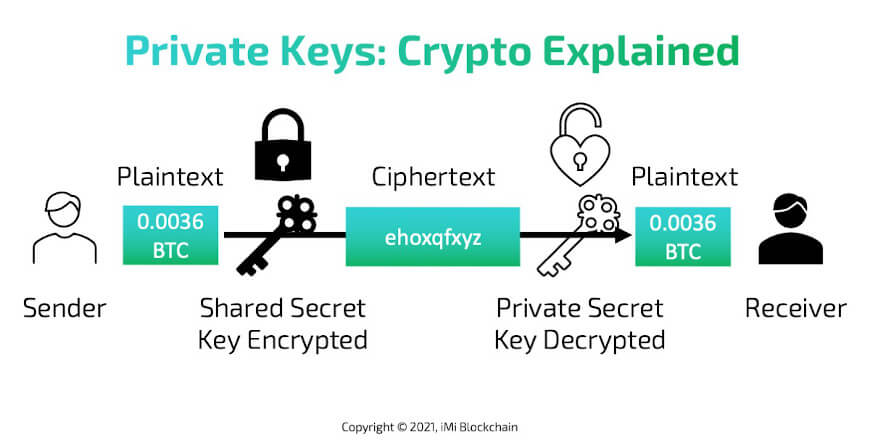
Share this Image on Your Site:
Cryptocurrencies enable secure online payments without the use of third-party intermediaries. Most cryptocurrencies exist on decentralized networks using blockchain technology—a distributed ledger enforced by a disparate network of computers. When you transfer cryptocurrency funds, the transactions are recorded in a public ledger. An advantage of cryptocurrency is privacy, as it allows you to make purchases without providing any personal information.
Your private key is your money in your pocket. Hence, to understand what is cryptocurrency, always keep your private key safe and never ever share this key with anyone.
Cryptocurrency Wallets
Just like you keep regular money in a wallet, you keep digital money (called cryptocurrency) in a special kind of wallet called a digital wallet. Everyone has their own unique digital wallet address. This lets people send and get digital money.

Share this Image on Your Site:
Digital wallets help keep your digital money safe. But, sometimes bad people find ways to steal from them. To keep your digital wallet safe, you can keep it in online storage (the cloud) or on your computer’s storage.
Mining
What is cryptocurrency mining? It is like a game where people use computers to earn new cryptocurrency coins. They do this by helping check and confirm transactions. These miners use strong computers to get new coins and sometimes also get extra coins from fees. They make sure there aren’t too many coins out there at once.
Staking
What is cryptocurrency staking? Imagine you have a special kind of money online, called cryptocurrency. There’s a way to earn more of this money by helping the system work. This is like putting your money in a bank, and the bank pays you some extra money as a thank-you (called interest). In the world of cryptocurrency, this is called “staking”. You lock up some of your coins, and in return, you get more coins over time. By doing this, you help make the system more secure and run smoothly. Just like how money in a bank helps the bank do its job, staking your cryptocurrency helps the online system work better.

Want to Build Wealth with Cryptocurrency?
Unlock the full potential of crypto investments. We teach you how to:
Manage Crypto Asset – trade, and store digital assets securely.
Minimize Risks – through insights on how to deal with volatility and security risks.
Build Wealth – with customized advice for your individual needs.
BOOK YOUR LIVE SEMINAR NOWFinite Supply
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, have a limited number of coins, and a finite supply. This helps keep their value. When the idea for Bitcoin was first shared by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, he said there would only ever be 21 million Bitcoins. Right now, over 18 million of those coins are already out there.
This makes cryptocurrencies a bit like gold and virtual currencies. There’s only so much gold in the world, so it keeps its value. But money made by countries (like dollars or euros) can be printed as much as they want, which can make prices go up over time. That’s why some people say cryptocurrencies are like gold and regular money can lose its value. The entire monetary worth of all the coins that have been mined is known as market capitalization. This concept is similar to the limited supply of gold, as it represents the total value of a cryptocurrency based on its price and the number of circulating coins.
Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies are not considered legal tender, meaning there is no requirement for them to be accepted as a form of payment for debts, public or private. Cryptocurrencies have become a popular tool with criminals for nefarious activities such as money laundering and illicit purchases. The case of Dread Pirate Roberts, who ran a marketplace to sell drugs on the dark web, is already well known. Cryptocurrencies have also become a favorite of hackers who use them for ransomware activities. To understand what is cryptocurrency, as a digital currency, serves as a medium of exchange, utilizing cryptography to secure and verify transactions, as well as control the creation of new units of a particular digital currency.
Cryptocurrencies are distinguished from fiat currencies like the United States dollar or the British pound because no central authority does not issue them, making them potentially impervious to government intervention or manipulation. In Europe, cryptocurrencies are legal in the European Union. Derivatives and other products that use cryptocurrencies must qualify as “financial instruments.” In June 2023, the European Commission’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation went into effect. This law sets safeguards and establishes rules for companies or vendors providing financial services using cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges are places where you can buy and sell digital money, like Bitcoin or Ethereum. These exchanges tell us how much digital money is worth compared to regular money, like dollars or euros.
Share this Image on Your Site:
You can swap one type of digital money for another, or trade it for regular money. Some exchanges even let you trade in other ways, like with special crypto products. For using these exchanges, you might be charged a small fee, usually less than 1%.
Some popular exchanges where you can do this are Binance, Coinbase, eToro, Gemini, and Robinhood. Robinhood lets you trade popular digital money like Bitcoin and Ethereum and usually doesn’t charge as many fees as others.
Investing in Cryptocurrency: Be aware of Volatility
Now that you know what is cryptocurrency, let’s talk about investing in it. Cryptocurrencies can increase in worth over time. This is why some people prefer them over regular ways of investing. A recent study by CNBC showed that 1 out of 10 people put their money in cryptocurrency. This might be because it’s easy to buy and sell these digital coins.
But, investing in cryptocurrencies can be risky. Their prices can change a lot very quickly. And there’s nothing real, like gold or money, backing their value.
You can buy cryptocurrency from other people or on special websites called exchanges. But, like with all ways to invest, it’s good to learn about it first.
If you want to know more about how to start with cryptocurrency, you can look up guides for beginners.
Cryptocurrency 101: How does Cryptocurrency Work?
What is cryptocurrency again? Exactly, it’s like digital money. Instead of being controlled by a bank or government, it’s managed by its users on a big online system. Think of it like virtual coins on the internet. So how does cryptocurrency work?
Bitcoin was the first type of digital money. There’s a limit to how many Bitcoins can be made – only 21 million. Since Bitcoin became popular in 2017, there have been many other types of digital money made.
When you have this digital money, you keep it in a special online pocket called a wallet. This wallet is locked with a special key (like a password). With this key, you can buy more digital money or sell what you have. And that’s how it works! Simple, right?
Cryptocurrency Types

To understand what is cryptocurrency, we have to dive into more details. According to a website called CoinMarketCap.com, right now there are more than 10,000 different kinds of digital money called cryptocurrency. Altogether, they’re worth about $2 trillion. We can split them into two main groups:
- Coins have their own special system (called a blockchain). Bitcoin is one of these. There are also others that aren’t Bitcoin, like Ethereum or XRP, and we call them Altcoins
- Tokens are another type of digital money, but they don’t have their own system like coins do
Coins
Coins in the digital world are like online money. The first one was called Bitcoin, made by someone named Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. After Bitcoin, other online coins were made using the same Bitcoin system. These are called “altcoins”. Some popular ones are Peercoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, Aurora Coin, and Namecoin.
However, not all coins use the Bitcoin system. Some have their own special systems. Examples include Ethereum, Ripple, New York Coin, Waves, and Counterparty.
Tokens
Tokens might not have value on their own, but they can be used to save value. They’re often given out during events called initial coin offerings. This is when people use coins they already have to get these new tokens as a reward.
There are three kinds of tokens: security tokens, utility tokens, and value tokens. They aren’t used like regular money, like dollars. Instead, they have special jobs or uses.
For example, Bitcoin and Ether (which comes from Ethereum) are types of tokens. We’ll talk more about different coins and tokens next.
Cryptocurrency Examples
Now we know what is cryptocurrency in detail. Therefore, let’s look at some examples. Ever since Bitcoin came out, lots of people have started using digital money called cryptocurrency. Every day, many types of this money are traded. Here’s a list of eight kinds of digital money that lots of people use, are active, and are worth more than $10 million each.
1. Bitcoin (BTC)

Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, was created in 2009 by someone (or maybe a group) using the name Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin (BTC) is like digital coins that don’t need a bank or government to work. It uses something called blockchain to keep track of all its transactions. Bitcoin, which launched in 2008, remains the biggest, most influential, and best-known payment system in the world. In the decade since, Bitcoin and other popular cryptocurrencies like Ethereum have grown as digital alternatives to money issued by governments, such as the United States. This means there’s no room for manipulation of transactions, changing the money supply, or adjusting the rules mid-game.
Several companies that sell tech products accept crypto on their websites, such as newegg.com, AT&T, and Microsoft. Overstock, an e-commerce platform, was among the first sites to accept Bitcoin. Shopify, Rakuten, and Home Depot also accept it. China has banned cryptocurrency exchanges, transactions, and mining within its borders, but has a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
By October 2023, there are almost 19 million Bitcoins out there, and they are worth about $538 billion altogether. When people use bitcoins to buy things, this is recorded in a big digital book. Some people, called miners, use strong computers to make sure all these transactions are correct.
Many people around the world know and use Bitcoin. Some places, like El Salvador, even say it’s like regular money. But there’s a problem: the computers that check Bitcoin transactions use a lot of power, which isn’t good for our planet.
2. Ethereum (ETH)

Ethereum, often called ETH or ether, is like Bitcoin’s younger sibling. It’s the second most famous digital money out there. People made it in 2015, and one of the main guys behind it is Vitalik Buterin.
Ethereum is special because it lets people set rules for money exchanges, kind of like a digital promise. These rules make sure people do what they said they would. If they don’t, the money can be given back.
Right now, some smart folks are working on making Ethereum even better and faster. This new version will be called Ethereum 2.0. It’s going to break jobs into smaller parts and use a new method to make sure all transactions are legit. This will save money and be better for our planet!
3. Litecoin (LTC)

Litecoin, often called LTC, is like an older sibling to many digital coins. Think of it as a cousin to Bitcoin. It’s faster in processing transactions and charges fewer fees than Bitcoin. It also has its own unique way of securing data. If you ranked cryptocurrencies by their popularity, Litecoin would be in the top three and has more coins available than most, totaling 84 million.
Back in 2011, a guy named Charles Lee, who used to work at Google, made Litecoin. He often said that Litecoin is like a “lighter” version of Bitcoin. The main differences? Litecoin creates data blocks quickly and uses a method called Script to prove its work.
People often say that if Bitcoin is like gold, then Litecoin is like silver. Litecoin can make 4 blocks in the time it takes Bitcoin to make just one! Since its start, Litecoin has added many new things but always kept it safe and honest.
4. Ripple (XRP)

Ripple (XRP) is like a digital money system that works really fast. People like it because you can easily change it into dollars, yen, euros, and other money types. There’s also a place within Ripple where you can do these exchanges. Ripple lets computer experts make their own ways to pay using its system.
Ripple started in 2012. Two guys, Chris Larsen and Jed McCaleb, made it. Jed also helped create another digital money system called Stellar and a place to trade called Mt. Gox.
Using Ripple, you can send money and it gets there super fast with hardly any fees. It’s so good that many big banks use it. Unlike other digital money like Bitcoin, Ripple is simpler. Besides just sending money, you can also use Ripple to trade assets and send money in ways like the SWIFT system.
5. Cardano (ADA)

Cardano (ADA) is like a new version of digital money, or cryptocurrency. It’s different because it uses a method called “proof-of-stake.” This is a special way to make sure everyone using the system is honest. In 2021, the price of Cardano went up a lot – it grew more than 16 times!
A man named Charles Hoskinson started Cardano. Before this, he helped start another digital currency called Ethereum. The main group that looks after Cardano is in a place called Zug in Switzerland. Instead of using a detailed plan (often called a “white paper”), they have some main ideas they follow. They want to solve problems that other digital money has, like being able to handle a lot of people using it at once.
Recently, Cardano made a big update called the Alonzo fork. This lets people make special contracts using the system.
6. Tether (USDT)

Tether (USDT) is like a digital dollar called a Stablecoin. It works on a system called a blockchain. One USDT is always equal to one U.S. dollar.
USDT started as “Realcoin” in 2014. It was created by Brock Pierce, Reeve Collins, and Craig Sellars. The company that manages it is in Hong Kong, but the people who run it also run Bitfinex, a place where people trade digital money, which is registered in the British Virgin Islands.
Tether works on systems like Bitcoin and Ethereum. The main idea of USDT is to mix the freedom of digital money with the steady value of the U.S. dollar. Stablecoins, like USDT, are used by people who invest in digital money to make their trading easier.
7. Dogecoin (DOGE)

Dogecoin (DOGE) is a type of digital money that started in 2013. It has a picture of a Shiba Inu dog, so many people recognize it. Some people think of it as a fun or “joke” coin.
Many people who know a lot about digital money are paying attention to Dogecoin. Even though people don’t use it for many things, it’s different because there’s no limit to how many Dogecoins can be made. This is different from Bitcoin, which has a limit. So, it’s interesting to see what happens with Dogecoin.
8. Binance Coin (BNB)

Binance Coin, or BNB, is a special digital coin that started in 2017. When people use it on Binance, which is a big place to buy and sell different digital coins, they can get cheaper fees. Binance is super popular, and people use it to trade more than 15 billion dollars every day!
Right now, BNB is one of the top 4 digital coins with a total worth of 65 billion dollars. Besides using it on Binance, you can also use BNB to buy things online, pay for stuff, plan trips, or get fun entertainment deals.
9. Solana (SOL)

Solana (SOL), a crypto platform that uses the proof-of-stake mechanism, has demonstrated its superiority in terms of transaction speed, with an average of around 3,000 transactions per second (TPS). This makes Solana much faster than the sluggish Bitcoin blockchain, where the average transaction speed is at least 10 minutes.
10. Stablecoins

Stablecoins are a type of digital cryptocurrency, like Bitcoin or Ethereum. But, while the value of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin can change a lot in a short time, stablecoins try to have a stable value. They do this by linking their value to something else that’s stable, like the US dollar. So, if you have 1 stablecoin that’s tied to the US dollar, it should always be worth about 1 dollar. This makes them useful for people who want the benefits of digital currency without the wild price changes. Examples are USD Coin (USDC), Binance USD (BUSD), or the above mentioned Tether (USDT).
So what is Crypto? Key takeaways
As we went through all the details you know now what is cryptocurrency. So what is crypto? It’s actually the same, just a short for the same digital money, but again, it’s different because no single group or government controls it. Think of it like this: regular digital money is controlled by a country’s government, but cryptocurrency isn’t. Bitcoin was the first one, but now there are lots of different types of cryptocurrencies.
This guide tells you the basic things about what is cryptocurrency. If you want to learn more, you can talk to one of our experts for free.
Learn all about Crypto!
Training in Small Classes
Webinars about Cryptocurrency
Crypto Courses at University Level
Free Cryptocurrency Tips!
Get monthly tips on Cryptocurrencies.
On top, you’ll get our free Blockchain beginners course. Learn how this technology will change our lives.
FAQ
Why are cryptocurrencies so popular?
Cryptocurrencies are getting really popular, and here’s why:
1. People think they’re the money of the future. They can be used in many ways and can grow in value. That’s why lots of folks want to buy them
2. They aren’t controlled by big banks. This is cool because banks often make money less valuable over time through something called inflation
3. They can move money fast and are really safe
Are cryptocurrencies legal?
Cryptocurrency rules are different in each country. Some places, like China, India, and Nigeria, don’t allow it. But in the U.S., it’s okay. If your country says no, you can’t buy it with your bank money.
Are cryptocurrencies a good investment?
Compared to a regular business that makes more money over time, cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, don’t have a set value. But, many people see them as a different way to invest in the cryptocurrency market, just like stocks or bonds. Some say cryptocurrencies could be really important in the future. However, they can be risky because of their price volatility, such as the rapid surges and crashes in value that occurred in November 2021.
So, if you want to invest in them, be careful! The Securities and Exchange Commission has raised concerns about the price volatility of cryptocurrencies, similar to their concerns about activities such as crypto staking and the operations of some large crypto companies. And, as with most other investments, if you reap capital gains selling or trading cryptocurrencies, the government wants a piece of the profits. How exactly the Internal Revenue Service taxes digital assets – either as capital gains or ordinary income – depends on how long the taxpayer held the cryptocurrency and how they used it. Scammers frequently use social media platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter to dupe consumers into making these investments.
Where can I go to learn more about how to invest in cryptocurrency?
You can learn more about cryptocurrency trading classes online, for example at the iMi Blockchain Academy. Some places where you buy and sell this money also teach you how when you sign up.
How can you use crypto assets to make purchases?
Did you know you can use your digital coins, like Bitcoin, to buy things now? Some big online stores, like Amazon and Overstock, let you use them. Even PayPal lets you buy, keep, and sell these digital coins.
In the U.S., there’s a card called BitPay. It changes your digital coins into dollars when you want to buy something. But be careful, because getting the card and taking money out at an ATM can cost extra fees.
Are cryptocurrencies financial sec, like stocks?
Whether the SEC will treat cryptocurrencies, or specific types of cryptocurrencies, as securities will be at the forefront of crypto regulation, and could have major implications for the asset class in the near future.
Is Cryptocurrency in India Legal?
Cryptocurrencies in India are like wild-west money. There’s no main group watching over them or making rules. If you use them, you’re on your own. If something goes wrong, there’s no one to help sort it out. So, if you decide to trade with this kind of money, be careful because it’s risky.


